What’s new in Blackboard March 2025
In the March update, Blackboard has changed how release conditions work with due dates and included the ability to copy banners from one course to another. Other updates include enhancements to Tests, Assignments, & Gradebook, and Discussions.
Release conditions panel: due dates now included
When instructors customise release conditions for a content item, the due date for the item is now included with the date and time fields.
Image 1: The due date of a content item now displays after the date and time fields

.
This means that due dates must be between the release conditions of Date/Time that have been applied.
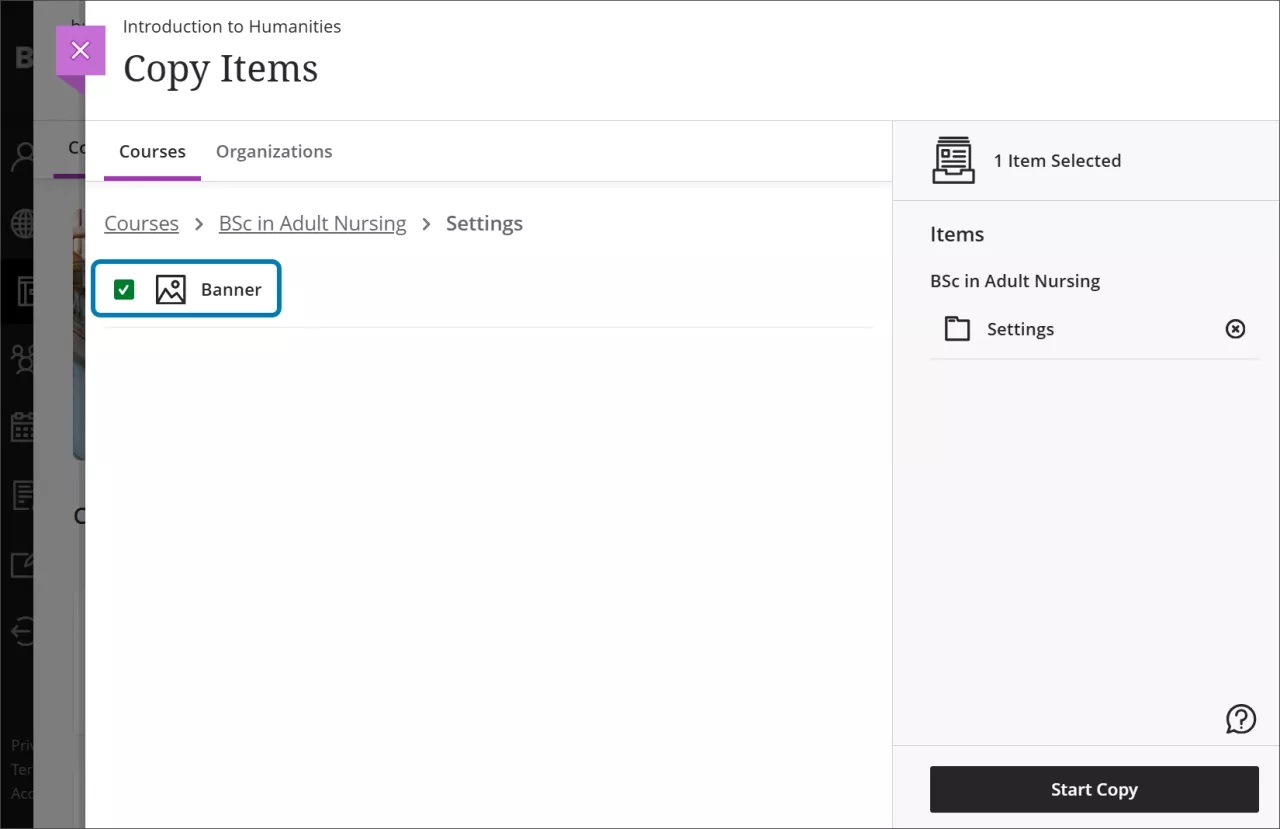
Copy banners between courses
Instructors now have the option to copy banners between courses. Banners can be copied from Ultra or Original courses.
Image 1: The Copy Items page now has the option to select the course banner under Settings
Follow the instructions on copying content for further information.
Tests, Assignments, and Gradebook
The following enhancements are grouped under tests, assignment, and gradebook activities.
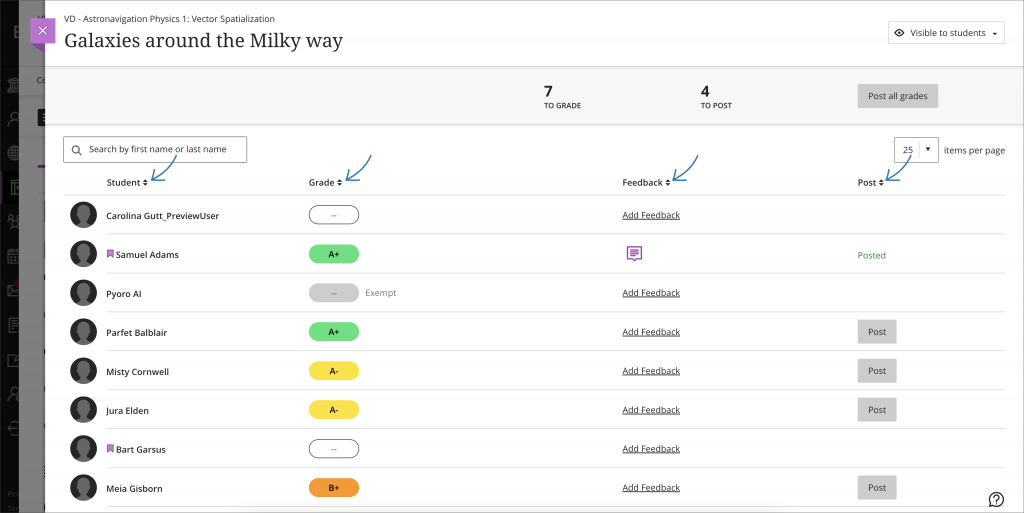
New student submission review page for tests
A new and enhanced student-facing submission review page for tests has been developed.
The new layout means that all feedback is clearly laid out and easy for students to identify.
Image 1: The student view of the graded test submission includes a submission timestamp, submission receipt, and feedback for individual questions.
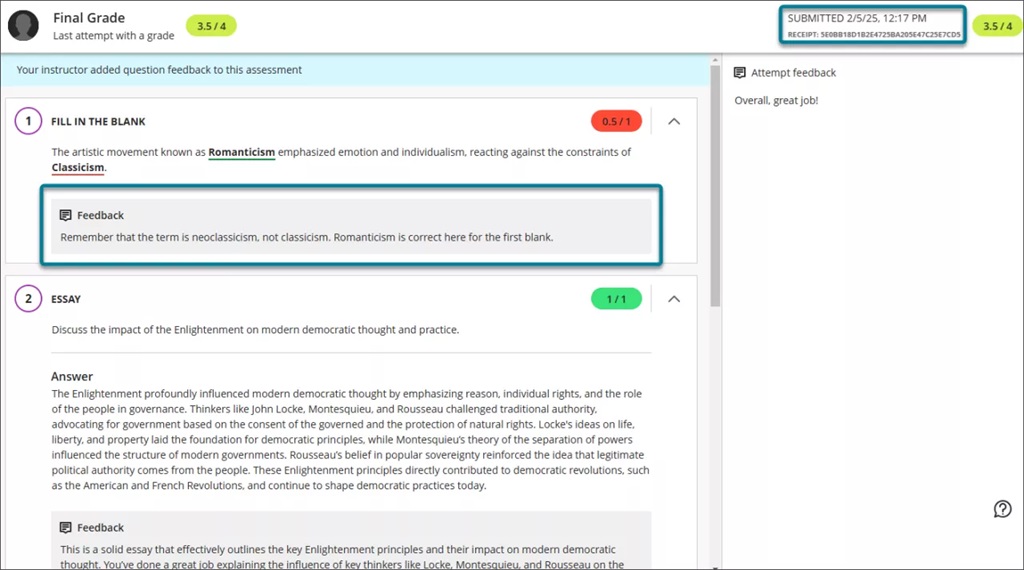
If the test is visible and feedback has been posted, students can access the review page from:
- The gradebook feedback button for the test
- The small panel that displays when students access a test from the Course Content page
If a student submits multiple attempts, they can review each attempt on the submission review page. The instructor defines which attempt to grade in the test’s final grade calculation setting.
Please note that this does not affect online exams as we advise that the test is hidden from students to prevent them seeing their results.
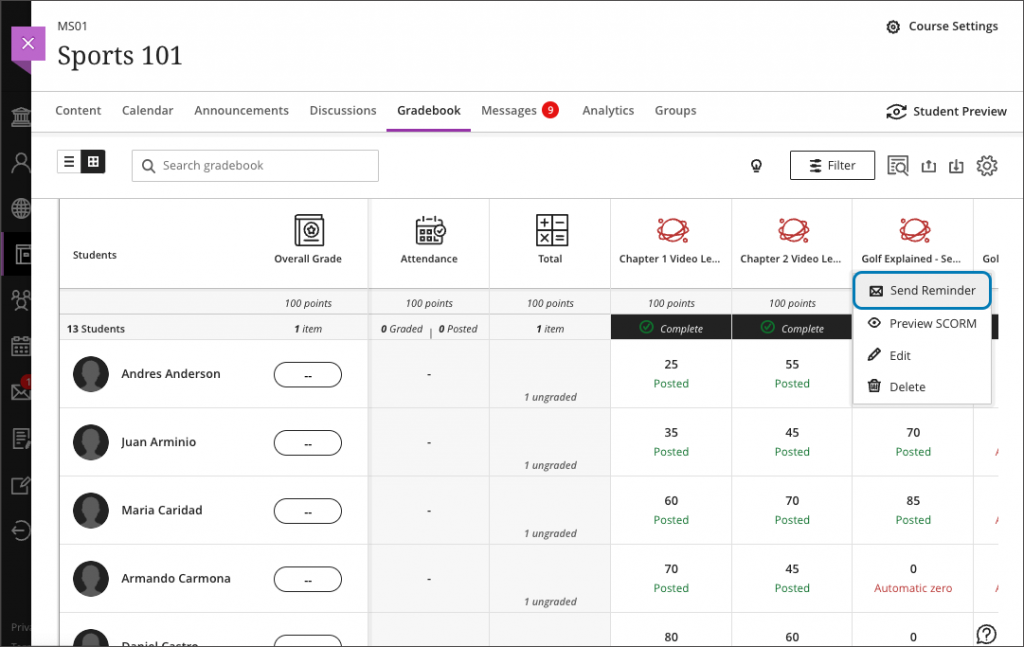
Show/hide calculated columns in the gradebook
Instructors can now configure visibility for calculated columns from Items Management in the Gradebook by click on the associated calculation:

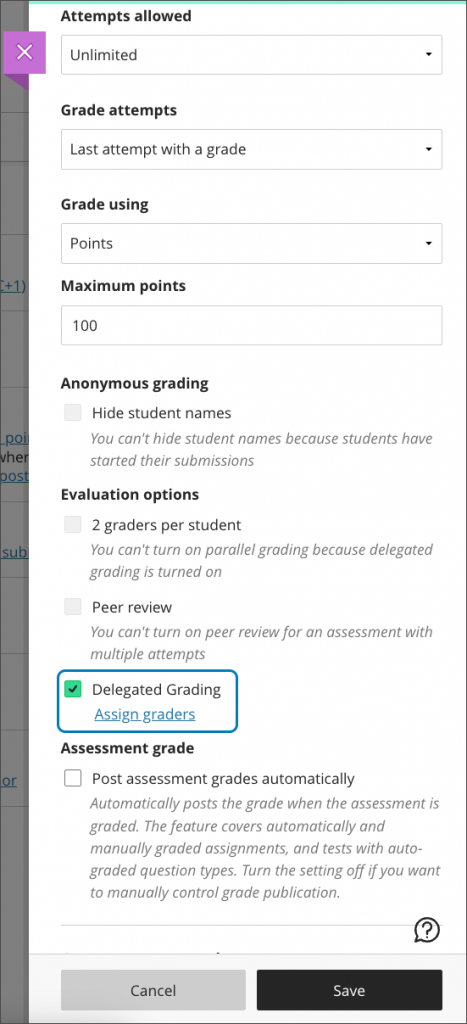
Pop-out rubric with Blackboard Assignment
Grading rubrics on Blackboard Assignments can pop out into a separate window as part of the assignment workflow.
Image 1: Instructors can pop out the rubric by selecting the expand icon in the rubric panel.
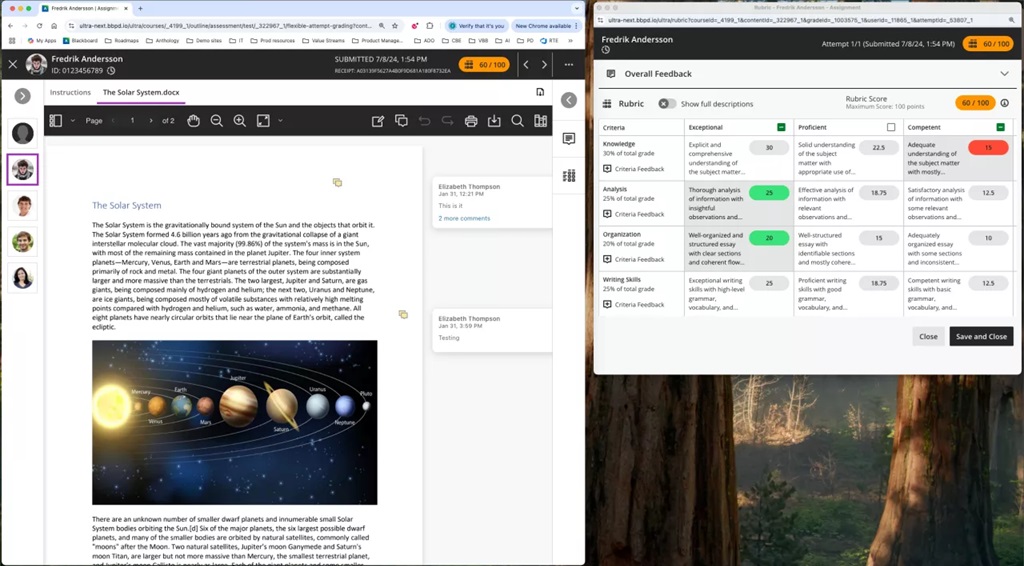
When the pop-out rubric is open, the ability to add Overall Feedback and grade with the rubric in the main grading interface is inactive. This prevents an instructor from editing the same information in two separate places simultaneously.
We recommend using two screens with this enhancement.
Discussions
Usability improvements for Discussions
Several improvements have been made to Discussions:
- Improved visibility: Posts now have a grey background to stand out better against the page.
- Full post display: Long discussion posts are now fully visible without the need for scrolling, enhancing readability.
Image 1. A long discussion post displayed in its entirety with a grey background.
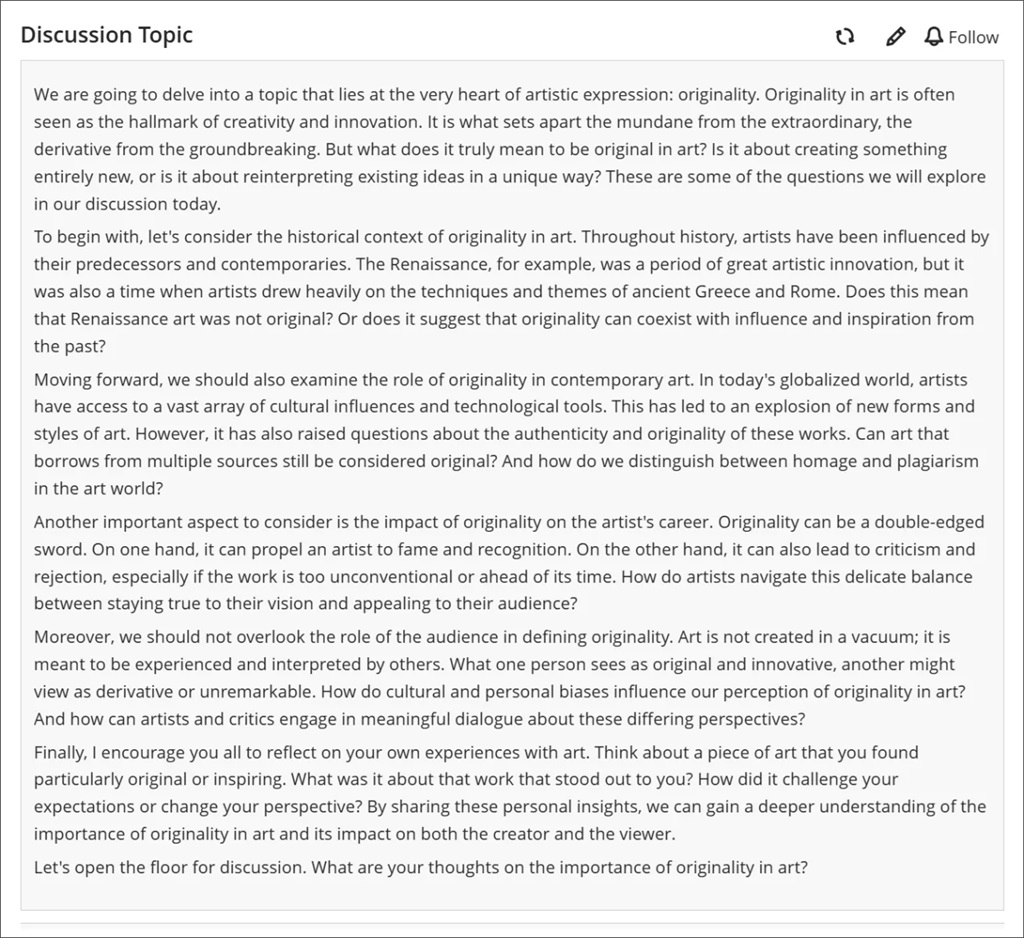
We made several changes to enhance the accessibility of key features on the discussion home page.
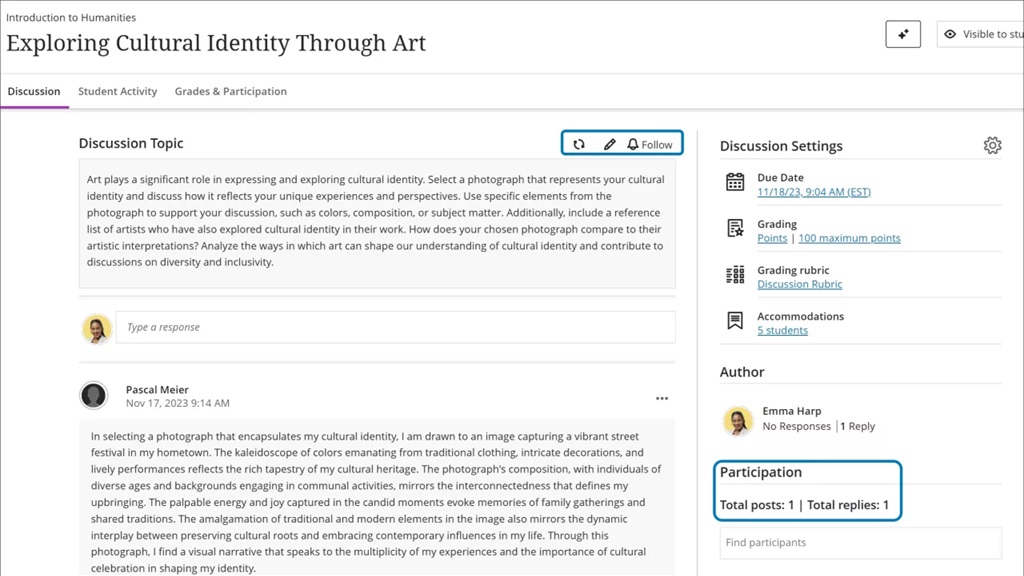
- Participation metrics: The number of posts and replies is now listed directly on the discussion home page, replacing the total response counter. This change makes important information more immediately available.
- Direct edit option: The Edit button is now directly accessible from the post, saving instructors time.
Image 2. The changes made to the discussion home page included the addition of an Edit button and a count of posts and replies.
Hidden Discussions tab from student course view
The Discussions page will only be available to students if any of the below conditions are met:
- Students have permission to create new discussions
- The instructor has created a discussion or discussion folder on the course
Anonymous discussions: New privilege to reveal author
System administrators can now reveal the identity of the author of an anonymous discussion post or reply. If you are running an anonymous Discussion and need to de-anonymise a comment, contact elearning@aber.ac.uk outlining the course, discussion, and post, as well as the rationale for requesting it be de-anonymised.
If you have any enhancements to request from Blackboard, please get in touch with us via elearning@aber.ac.uk.